In the ever-evolving landscape of digital assets, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) have emerged as a revolutionary technology, enabling the ownership and transfer of unique digital items. From digital art and collectibles to tickets, contracts, and in-game items, NFTs have captured the attention of artists, creators, and investors worldwide. However, with the growing interest in this unique market comes a pressing concern: the security of NFT digital assets.
Theft, piracy, and copyright infringement are significant issues plaguing the NFT ecosystem. These issues go beyond the violation of intellectual property rights and have strong financial repercussions. When NFT content is stolen or pirated, the uniqueness and value associated with the assets are greatly degraded. This not only undermines the trust and confidence of NFT creators and collectors but also can result in substantial financial loss.
Numerous high-profile cases have highlighted the vulnerabilities surrounding NFT content and the urgent need for robust and scalable security measures. For example, pirates gain unauthorized access to the original content and distribute it freely or sell it without the creator’s consent.
As a result, the value and exclusivity of the NFT are diminished, impacting both the financial returns for creators and the perceived value for collectors. July 2022 saw over 4,600 NFTs stolen – the highest month on record – indicating that scams have not abated despite the current crypto bear market (Elliptic. NFT Report, 2022). These incidents underscore the importance of implementing effective security measures to protect the integrity and value of NFTs.
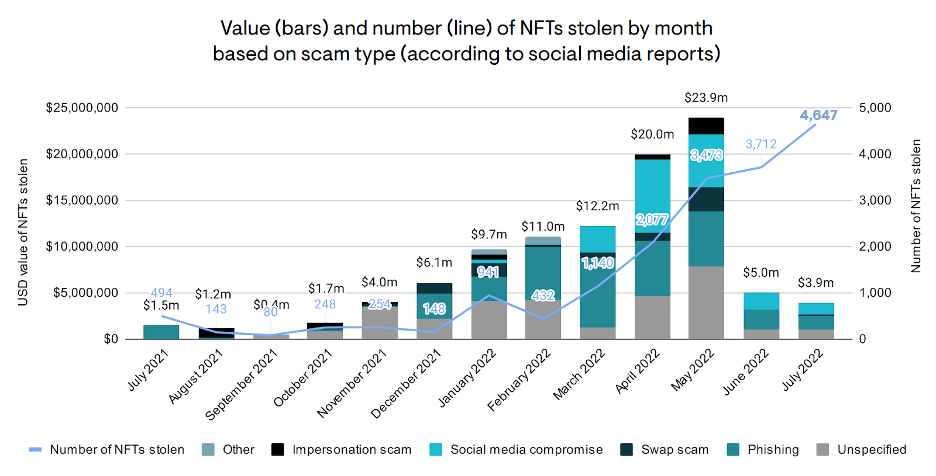
Source: https://www.elliptic.co/hubfs/NFT%20Report%202022%20-full.pdf
In this blog post, we delve into the challenges surrounding NFT security and explore the existing ways to mitigate the risks of illegal downloads and piracy. We also discuss the critical role of integrated solutions in enforcing Web3 platform security by introducing Intertrust MarketMaker.
With a more thorough understanding of the current state of NFT security and potential solutions, market participants can better understand their options as they navigate the evolving landscape of digital assets while safeguarding the interests of creators and collectors alike.
The Illusion of NFT content security
While NFTs offer ownership to and create scarcity for digital assets, it is essential to recognize that the content associated with NFTs is not entirely secure. Despite blockchain’s inherent security, the underlying content associated with the NFT token is not solely reliant on blockchain technology for security. The content itself, whether it is a digital artwork, a music file, or other types of virtual items, is typically stored off-chain, often on centralized servers or decentralized storage platforms.
This raises various concerns; while the ownership and transfer of NFTs are recorded on the blockchain, the actual content is stored separately, and it is susceptible to unauthorized access or hacking. If unauthorized individuals gain access to the original content, they can potentially duplicate or distribute it without the creator’s consent, undermining the exclusivity and value of the NFT. As self-reported by OpenSea, more than 80% of its NFTs were unoriginal or fake (Sports Business Journal, 2022), highlighting the widespread problem of illicitly duplicated NFTs circulating in today’s market.
The distribution of NFT content poses additional challenges. Once access to content associated with an NFT is granted, typically it can be copied, shared, and redistributed without any restrictions. So, even legitimate distribution of NFT content can expose creators and rights owners to the risk of piracy. To truly protect artists’ copyrighted work and maintain content rights to preserve the long-term value of NFTs, it is crucial to develop robust security measures that extend beyond the blockchain and address the limitations inherent in current content protection solutions.
Overview of current protection mechanisms:
Watermarking and metadata: Content creators often utilize watermarks and metadata to discourage unauthorized duplication. Visible or invisible watermarks can be embedded within digital files, providing a unique identifier for the file.
Metadata, such as copyright information and licensing terms, can also be attached to NFTs, enabling creators to assert their rights and specify authorized usage. While these protection methods offer some level of deterrence, they are passive and can only help with remedies such as takedown notices or lawsuits after the content has been duplicated without permission. They can also be removed or tampered with by determined individuals, compromising the integrity of the content. Accordingly, watermarking and metadata should be thought of as only a partial solution
Encryption and decryption: Encryption is defined as the process of converting content into an unreadable format using cryptographic algorithms. Encrypting NFT content can help prevent unauthorized access during storage and transmission. It makes it difficult for unauthorized individuals to gain access to original files. However, once the content is decrypted, it becomes susceptible to piracy.
Image recognition software (AI): Image recognition software is an advanced security approach that uses artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to analyze and identify specific visual patterns within images.
By incorporating image recognition software into NFT distribution platforms, the software can scan and compare uploaded or shared images against a database of known copyrighted or protected content. If a match is found, it can trigger an alert or restriction, and prevent the unauthorized usage or distribution of the content.
In the context of NFT content security, image recognition software can be used as a preventive measure against the unauthorized use or distribution of copyrighted or protected content. However, image recognition software, while a valuable security solution, has significant liabilities including false positives, false negatives and evolving techniques to circumvent detection. These can limit accuracy and introduce privacy concerns and potential bias. Moreover, image recognition software does not prevent the distribution of pirated content on platforms that do not use it.
In-house DRM: Digital rights management (DRM) is a traditional method for protecting digital content with a proven track record. Custom DRM solutions are being adopted by some NFT distribution platforms. This involves building a DRM system tailored to the specific needs and requirements of the platform or marketplace, rather than relying on third-party DRM solutions.
Even though in-house DRM solutions can provide a higher degree of control and customization for content security, they face significant challenges in achieving seamless interoperability with multiple consumption platforms, devices, and file formats. As the number of platforms, devices, and content offerings expand, continued development of an in-house DRM solution to ensure scalability and enforcement effectiveness is challenging.
Finally, in-house DRM creates a dependency on internal resources, limiting the organization’s ability to adapt quickly to changing market demands, incorporate new features or security enhancements, and take advantage of advancements in DRM technologies developed by third-party vendors.
To truly protect artists’ and content rights and preserve the long-term value of NFTs, it is crucial to develop robust security measures that extend beyond the blockchain and address these limitations inherent to other content protection solutions.
Introducing Intertrust MarketMaker: An innovative solution for NFT security
As Web3 marketplaces continue to evolve, there is a growing need for innovative approaches that enhance asset monetization, reduce vulnerability to value losses, and overcome limitations in NFT protection methods. Intertrust MarketMaker addresses these challenges by seamlessly integrating ExpressPlay’s multi-DRM solution, a trusted and highly scalable DRM service used by leading commercial video streaming services and media companies around the world.
The integration of ExpressPlay DRM within MarketMaker introduces an extra layer of security into NFT platforms by encrypting the NFT assets and safely storing the keys needed to access them. MarketMaker also provides a highly-flexible approach to set policies to allow greater access to assets and foster innovative business models.
This not only protects NFT assets from unauthorized access and piracy attempts but it offers consumers flexible access to content without having to resort to piracy. With the protection offered by MarketMaker, rights holders gain the freedom to create NFT marketplaces tailored precisely to their desired opportunities. MarketMaker allows NFT assets to be wrapped with highly-effective security and usage policies on the fly, empowering distributors to make NFTs an integral part of their day-to-day business operations, enabling them to seize new possibilities with confidence.
By leveraging the power of ExpressPlay to seamlessly work with multiple industry-standard DRM technologies across a variety of consumption platforms, MarketMaker protects content creators and distribution platform operators with comprehensive security measures for their NFTs.
Robust encryption, rights management, and access control ensure that NFT content remains protected throughout the entire distribution process. Whether accessed through embedded website items, streaming, or downloads, NFT assets are safeguarded. MarketMaker also offers policies that allow offline playback and device-to-device side loading, providing flexibility for content distribution and consumption.
MarketMaker’s integration of ExpressPlay’s multi-DRM solution with the advantages afforded by blockchain recorded tokens elevates the security standards in Web3 platforms, providing content creators and platform operators with the tools to protect their NFT assets, explore innovative monetization avenues, and unlock the full potential of the Web3 marketplace landscape.
Conclusion
NFT security is a critical concern in the ever-evolving landscape of digital asset distribution and consumption. The vulnerabilities surrounding NFT content, such as theft and piracy, pose significant risks to the value and exclusivity of these assets. Typical asset protection mechanisms like watermarking and metadata have limitations, while in-house DRM solutions face challenges related to interoperability and scalability.
To address these challenges, Intertrust MarketMaker offers a comprehensive solution by integrating ExpressPlay’s multi-DRM technology with NFT tokens. This powerful integration ensures robust encryption, rights management, and access control for NFT content across various platforms and devices. With MarketMaker, content creators and platform operators can enforce security measures throughout the lifecycle of their NFTs, protecting against unauthorized access and piracy attempts.
By adopting MarketMaker, rights holders can create NFT marketplaces tailored to their specific needs, with confidence in the security of their assets. This integration eliminates the complexities associated with in-house DRM solutions, providing a scalable and interoperable solution for NFT protection.
Intertrust MarketMaker, with its integration of ExpressPlay’s solution, sets a new standard for NFT security in Web3 platforms. It empowers content creators, protects their assets, and enables them to explore new monetization avenues in the dynamic and evolving NFT marketplace landscape.